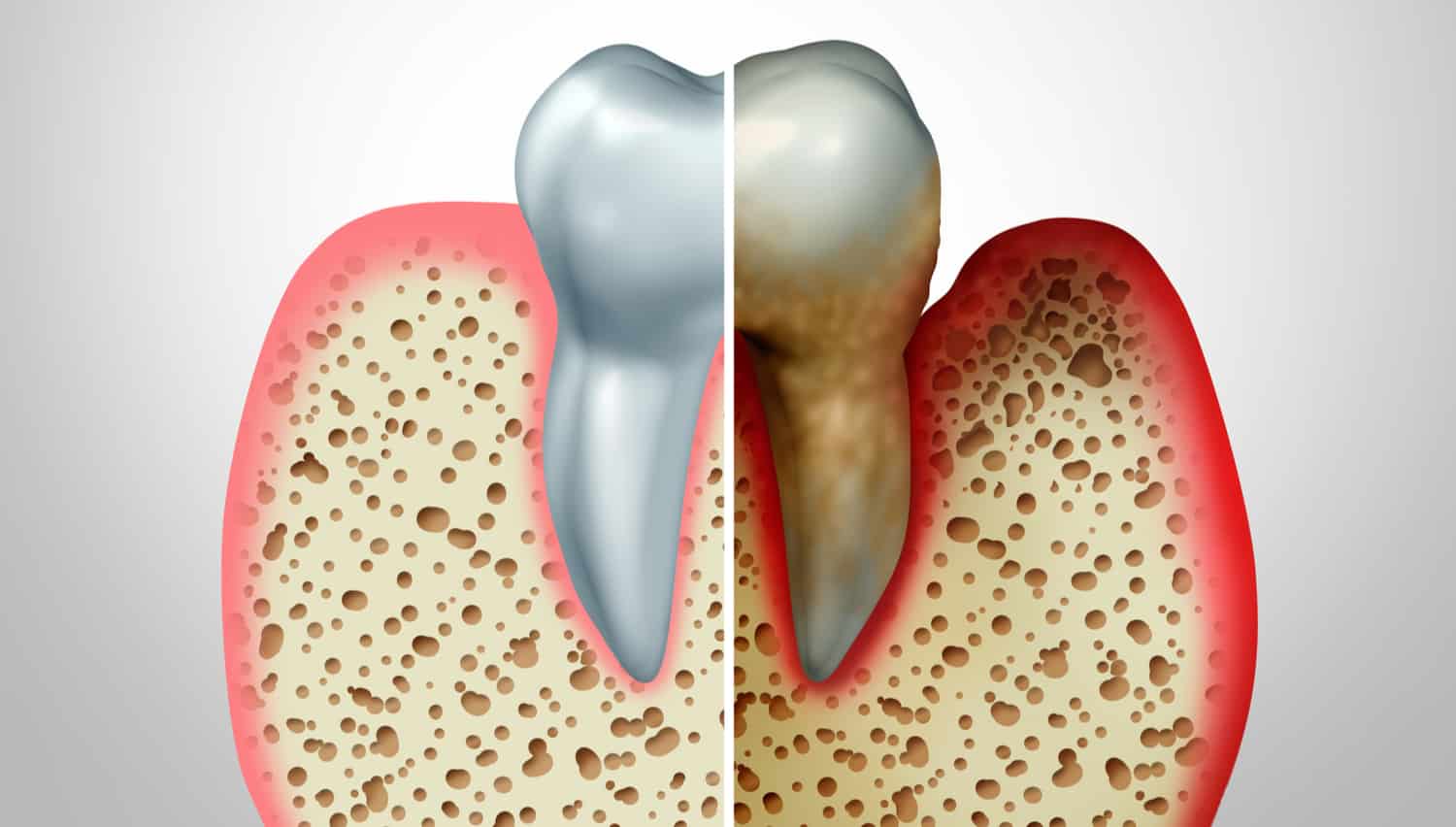
Dental bone loss can have serious consequences for your oral health and the appearance of your smile. Bone loss in the jaw is more common than you may expect and cannot be reversed without extensive bone grafting treatment. As a result, it’s important to understand why dental bone loss occurs and take the necessary steps to prevent it.
Effects of Bone Loss
Bone loss can cause your teeth to shift. This can result in a crooked smile and/or crowding. Nearby teeth may also become looser and eventually fall out. This leaves you vulnerable to infections and disease. Advanced bone loss can also change the shape of your face, and will often make you look older prematurely.
Cause – Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is the most common cause of dental bone loss. This condition is very prevalent, with a recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showing that 47.2% of adults over 30 have some form of gum disease. Earlier stages, such as gingivitis, do not cause bone loss, but they can progress quickly if left untreated.
Preventing Bone Loss from Gum Disease
It’s important to schedule regular check-ups with your dentist. This way, you will know early on if you are showing signs of early gum disease and can get treatment right away. Depending on the stage of the disease, this may involve scaling and root planing to clean out the area under the gums.
Cause – Tooth Loss
When you lose a tooth or have the tooth extracted, the root is no longer placing pressure on your jaw when you eat. Over time, this results in resorption of the bone. After only the first year, patients typically lose 25% of the bone, and this only rises from there.
Preventing Bone Loss After Tooth Loss
A dental implant is a titanium post that acts as an artificial tooth root. The implant puts pressure on your jaw and prevents resorption of the bone. Using an implant topped with a crown is the best way to prevent bone loss after losing a tooth while also restoring the appearance of your smile.
If you have lost most of your teeth, implant dentures are a great option and protect the health of your jaw compared to traditional dentures, which can sometimes accelerate bone loss.
Restorative Dental Care in Oro Valley, AZ
At Smith Dentalworks, we can help restore the appearance of your smile after losing a tooth. We partner with a trusted oral surgeon with dental implant placement, which helps prevent bone loss while also giving you a beautiful new smile. We craft restorations that match the surrounding teeth, look great, and preserve your oral health.